1. Introduction
This study examines the risk areas of potential wildfires in Los Angeles County. A Geographic Information System was used to determine areas that are both low in precipitation and high in fuel loads. Environments that are prone to fire are so largely because of three components. The fuel which is the potential vegetation that is at risk of being burned—included is how dry it is and how much there is (fuel load); The weather component, which is mainly attributed to the precipitation in a given area; and the third component is the topography, which is the slope and terrain and barriers. Fuel loads are very influential in determining and understanding potential fire zones, how long they could potentially burn for. The amount of vegetation is the major factor in determining fuel load as well as the dryness of the vegetation. The fuel Load has a major impact in terms of determining the intensity of the fire and how difficult the fire is going to be to control if the area were to burn (Keeley et al 1999). Weather is another key component that greatly affects the potential risk of a wildfire. Meteorologists and climatologists aided with recent technological advancements in remote sensing technologies are working on and studying new ways to understand our atmosphere and local weather systems to determine that future fire risk will increase with climate change (Cheeney, 1993). The effect of rainfall has to dampen the fuel largely depends on the size of the fuel; fine fuels absorb moisture more quickly than coarse fuels. Lack of precipitation is the most significant factor in contributing to the reduction of moisture levels in fuels (Keeley et al 1999). The effect of topography on rural fires can be significant, with slope being the most critical component. The slope can actually help accelerate the rate of the fire (Keeley et al 1999).
2. Methods
2.1 Study Area
The study area of Los Angeles County located between 34° 3′ 0″ N latitude, 118° 15′ 0″ W Longitude (fig . 1) has a total land area of 4,083 sq mi and peak elevation of 10,068 ft. The county is divided west-to-east by the rugged San Gabriel Mountains, filled with coniferous forests as well as other diverse vegetation in the surrounding areas that make Los Angeles a unique case study area.
2.2 Precipitation
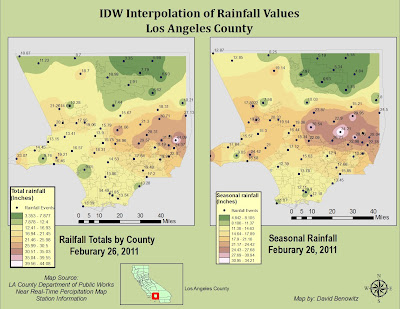
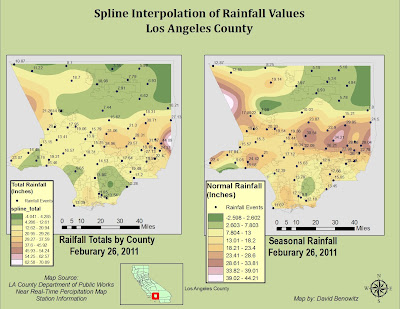
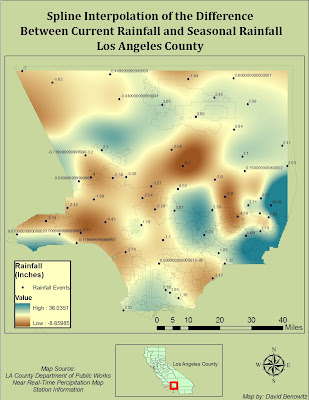
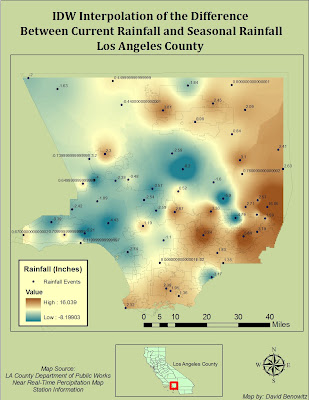
Precipitation data was obtained from 148 Manually Observed Non-Mechanical Rain Gages, these gages are measured once daily by volunteers and reported monthly. The Data used in the study was obtained from the USGS Beginning on 10-01-2010 and Ending on 03-16-2011 03:38 PM (fig.2). The table was converted to a usable formant and converted to a DBF. In ArcGIS it the gages were plotted and its Total Rainfall values were interpolated using an IDW interpolation to create a county-wide expected rainfall map.
2.3 Fire Fuel
Fire fuel data was extracted from a database of Los Angeles County Fire Department (FRAPS database). The type of fire fuel was not discriminated against and includes both natural vegetation and human constructed fuel. The fuel data was masked to only fit the Los Angeles County boundary.
2.4 Elevation/ Topography
Elevation data for Los Angeles County was obtained from the USGS Seamless Server as a raw 30m by 30m with a UTM coordinate system Digital Elevation Model. The DEM was converted to a Hillshade in ArcMap where it served as the underlying layer of the map.
2.5 Map Points.
A list of fire stations was obtained from the Los Angeles Fire Department locator website. These addresses were compiled into a spreadsheet (fig. 3 ) were they were geocoded to the LA County Streets Layer. In order to properly geocode the points, and address locator and geodatase were constructed from the Streets Layer using ArcMap. Note that the Street Layer is not visible. The hospital and recreation points were used from the Los Angeles county Enterprise GIS Database and were simply overlaid unedited.
The Projected Development layer was used from the FRAPS database and is used to represent areas of current and potential development by the year 2040. Development includes but housing and industrial. The Significant Ecological Area layer was obtained from the Enterprise GIS Data base and projected unedited.
1.1 Spatial Analysis
The Rain gages were interpolated using an IDW interpolation from 148 data point gages sensing total rainfall. The interpolation was in GRID formant with 32 Bit pixel Depth in WGS 1984 coordinate system. The Fuel Rank Layer was in both a different coordinate system as well as a different pixel size. The Fuel Layer was converted to match the interpolation layer pixel size. In the Raster Calculator the two layers were merged using a weighted average. Because this case study is looking for lack of rain instead of total rain, it was multiplied by (-.4) while the fuel rank was multiplied by (.7) giving more weight to the fuel than the rain (Fig 4).
A 3 mile buffer was given to the fire station point because 15 min is the estimated response time needed contain a fire before it gets out of control and 3 miles of travel takes roughly 15 minutes depending on the terrain traveled (FRAPS). A hillshade was under-laid to give the map texture and show points of high elevation that may be difficult to get to or increase the acceleration of the fire.
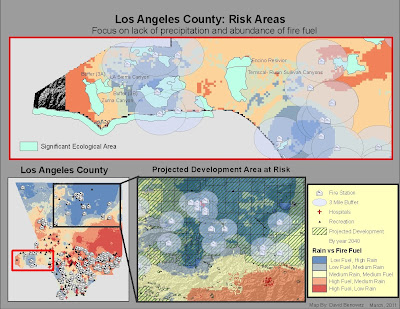
Results
Using the map that I created I found it appropriate to focus in on certain areas that I felt needed to be protected from fire Hazards. The area focused in on The Malibu- Encino area (West of the 405 Highway) shows many Significant Ecological Areas. There are two areas that are in Hazardous areas and not within 3 miles a fire station. The area in the middle of scene is comprised of the Encino Resivior and Temescal- Rustic- Sullivan Canyons. The Area on the left of the scene is comprised of Zuma Canyon, Upper LA Sierra Canyon, and Buffers 3A and 3B.
The scene on the map that depicts the North-East region of the county shows an area that is not at risk of a potential hazard because it is a zone that has neither low precipitation nor is it rich in fire fuel. There is a layer of Projected Growth overlaid on the hazard map that depicts an estimated growth in populated areas by the year 2040 based on recent census data. In this scene of projected development there is an area that currently lacks any fire station or hospital in a 9 mile radius.
Conclusion/ Discussion
This study shows that a Geospatial Information System is crucial to both protecting current endangered habitats as well as highlighting areas that are safe for future developments from wildfire hazards. The Hazard map is weighted to give stronger consideration to the fuel of the fire because no matter how little precipitation there is, there cannot be a fire if there is nothing to burn. The Vegetation in California is typically dry and conducive to burning, but will have a less chance of burning if it is a wet season because the vegetation will be healthier.
The Study area of the Malibu-Encino region shows that there is not fire station within a 5 mile area of the Temescal- Rustic- Sullivan Canyons. This is a practically important area because the North end of the canyon is owned by SoCal Gas to run a natural gas pipeline to more developed areas of Brentwood and Malibu. The rest of the Ecological zone is Sullivan Park owned by the state. The reason for the high fuel load is due the abundance of Sycamore trees which are known for their commercial use as fire wood. If there were to be a fire that reached a leaky pipe, the results could be disastrous. Just above the Sulivan Canyon is the Encino Resivior, I propose a fire station just the north in Encino city should be built to capitalize on the Reservoir’s water supply. If there were a fire the reservoir could be used by helicopters and planes to suppress the fire.
The Projected growth study are consists mainly of Palmdale and Unincorporated Los Angeles. These areas did see an increase in population up until the current recession, but have since taken a hit. The reason these areas remain largely uninhabited despite their lack of fire risk is because they also lack the other resources that make areas habitable. If future development were to occur, there would need to be more hospitals built, especially near the lone recreation site.
On the scene that shows the entire Los Angeles County, the part that sticks out the clearest in in the Mid-East of the county. This area was the source of the Los Angeles Station Wildfire that consumed much of Los Angeles in 2007. This area is largely forested and high in elevation so it is depicted as Red. Most of this area is state-owned with little development, but there are people on the outlying parts of the forestry extent.
There is still further GIS analysis that could be done with this study, most notably including wind data and well as history of seasons could be applied. With the addition of that information, we would have a more complete fire hazard map.
Sources:
Keeley, Jon E, and C J. Fotheringham. "Historic Fire Regime in Southern California Shrublands." Conservation Biology. 15.6 (1999): 1536-1548. Print.
Keeley, Jon E, and C J. Fotheringham. "History and Management of Crown-Fire Ecosystems: a Summary and Response." Conservation Biology. 15.6 (1999): 1561-1567. Print.
California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection's Fire and Resource Assessment Program (FRAP)
Los Angeles County Enterprise GIS
UCLA Mapshare
USGS Seamless Server
USGS Hydrology